Home – Lorrca
Lorrca
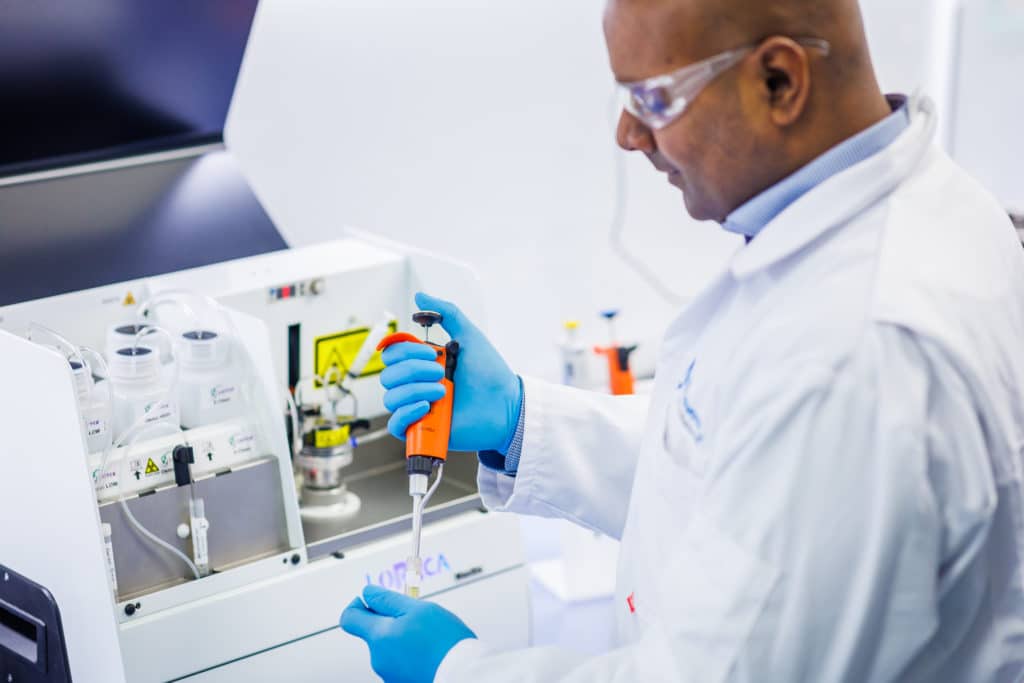

Hereditary Anemia
RBC membrane disorders
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherocytosis | |||||
| Elliptosytosis | |||||
| Xerocytosis | |||||
| Ovalocytosis | |||||
| Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis (SAO) |
Hemoglobinopathies
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sickle cell disease (SCD) | |||||
| Thalassemia |
Enzymopathies
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G6PD deficiency | |||||
| Pyruvate Kinase deficiency |
Acquired anemia
Infections
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sepsis | |||||
| Malaria | |||||
| Auto Immune hemolytic anemia |
Mechanical RBC lesions
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial heart valves | |||||
| Hart Lung machine | |||||
| Dialysis | |||||
| Sports medicine |
Storage lesions
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC-quality (bloodbanks) | |||||
| Cultured RBC quality |
Therapeutic RBC carrier
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Blood Cell Therapeutics |
Fundamental research
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC oxydative stress |
Medicine development
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro efficacy testing | |||||
| Safety evaluation |
Veterinary
| Deformability | Osmoscan | Oxygenscan | Cell-membrane stability | Aggregation/Disaggregation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparing species |
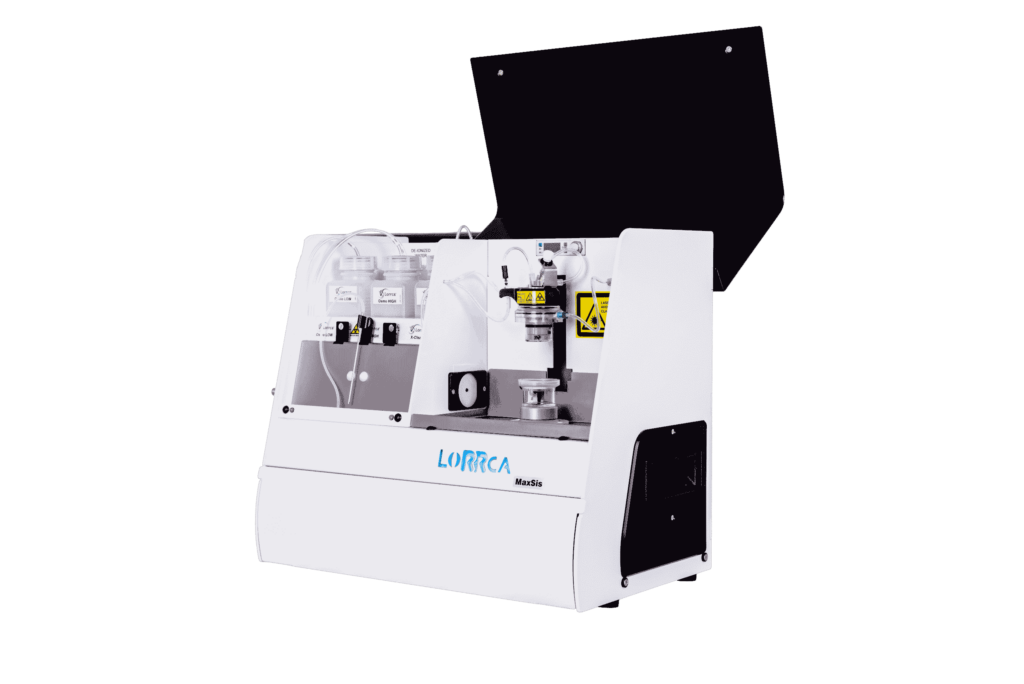
Use of the Lorrca
Examples can be categorized as follows:
• Hereditary anemia (hemoglobinopathies, enzymopathies, membrane disorders)
• Acquired anemia (mechanical hemolytic anemia and anemia caused by infections)
The table below combines several diseases and applications with specific Lorrca measurements.
Possible applications of the Lorrca RUO platform
The blood capillaries in organs are about half the diameter of an RBC. For sufficient perfusion of organs, RBCs need to squeeze through the capillaries. RBC deformability is an indicator for the perfusion quality and survival of RBC in all RBC research.
For this test, blood in a buffer is sheared between two concentric cylinders. A known shear stress is applied to the cells, resulting in deformation. This process is measured by a laser diffraction pattern, captured by a camera, and analyzed by dedicated software. The output is a characteristic graph.
The Osmoscan measures deformability along an osmotic gradient. This test is considered the gold standard in differentiating between spherocytosis and dehydrated-xerocytosis. Many RBC disorders are distinguished by their characteristic Osmoscan curve.
For this test, blood in a buffer of varying osmolality is sheared between two concentric cylinders. A known shear stress is applied to the cells, resulting in deformation. This process is measured by a laser diffraction pattern, captured by a camera, and analyzed by dedicated software. The output is a characteristic curve.
The Oxygenscan is a distinctive technique to quantitively measure and visualize RBC elongation under shear stress along an oxygen gradient.
The Oxygenscan measures the oxygen pressure at which the hemoglobin of sickle cell patients starts to polymerize, the Point of Sickling (PoS). This is a critical oxygen level at which the RBCs from SCD patients start to lose their deformability. This PoS is a phenotypic characteristic for each individual sickle cell patient and representative of its status and treatment efficacy.
RBC aggregation is an important, shear dependent, determinant of blood viscosity. It is a measure for the perfusion capability independent from the RBC deformability. Via syllectometry (i.e., laser backscatter versus time), the method allows the measure of the kinetic parameters of the aggregation process. The Lorrca aggregation and disaggregation measurement is used in research of infectious diseases, blood storage and blood quality, vascular pathologies, and tissue perfusion research.
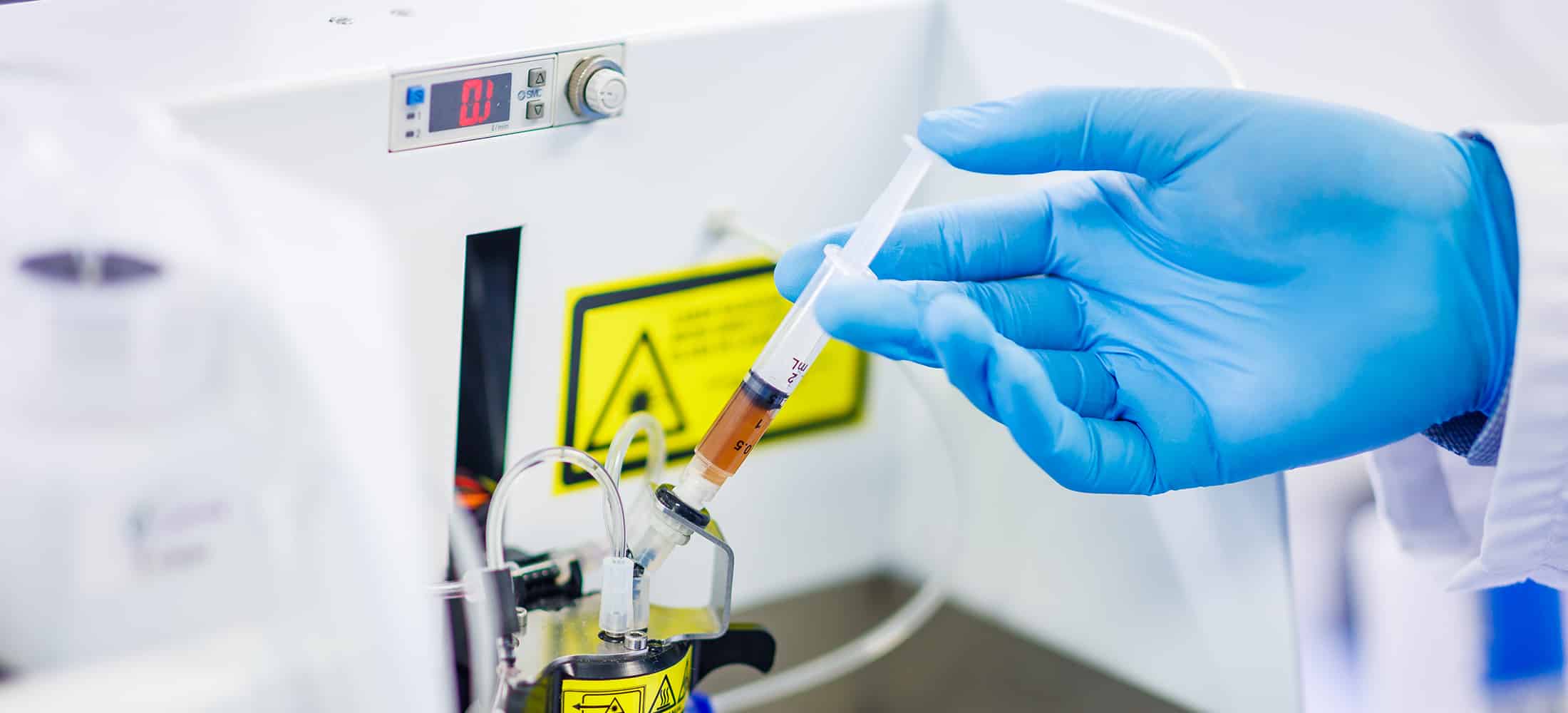

Find out more about our fields of research

Purchasing a Lorrca
An enquiry for a Lorrca usually comes with application questions on how the measurements might fit and add to your research objectives. Our specialized Lorrca business development team and our application specialists are knowledgeable and happy to work closely with you, while respecting the confidentiality of all our users.
Operator training
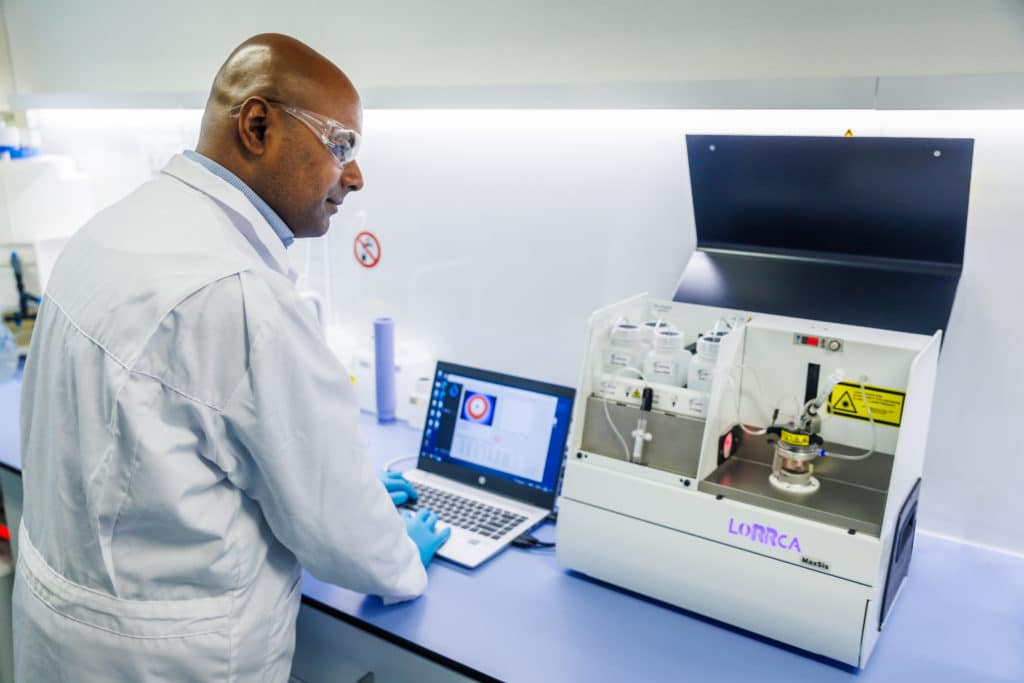


Support at hand
Lorrca is a technical product. When using it, system specific questions of technical or scientific nature may arise. The RRM Support team is specialized in answering these questions to keep performance to the highest standards.
Global distribution and service